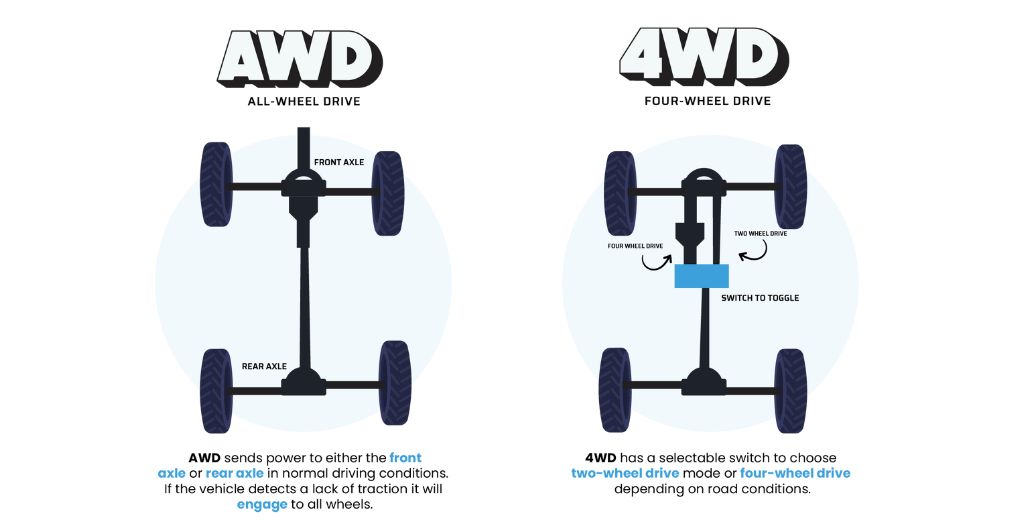
Car terminologies such as four-wheel drive and all-wheel drive can be confusing. Let’s delve into the key differences between these concepts in modern cars.
Four-Wheel Drive: The Part-Time System
- Definition: Four-wheel drive mechanically engages all four wheels and is commonly seen in modern-day SUVs designed for off-road use.
- Activation: The driver must push a button or pull a lever to engage the four-wheel drive system.
- Power Distribution: In this system, power is primarily sent to the rear wheels, while the front wheels spin freely.
- Intended Usage: Four-wheel drive is advantageous in challenging terrains, providing increased traction and control.
All-Wheel Drive: The Full-Time System
- Definition: All-wheel drive powers both the front and rear wheels at all times.
- Mechanism: An electronically controlled clutch or similar mechanism allows for a rotational difference between the front and rear axles.
- Activation: All-wheel drive is always “on” and does not require manual engagement by the driver.
- Power Distribution: The system adjusts power distribution based on road conditions, sending more power to the rear wheels for fuel efficiency on regular highways, and distributing power evenly across all four wheels in adverse conditions.
- Advantages: All-wheel drive offers enhanced traction and helps prevent wheelspin in various driving situations.
Advantages and Considerations
Four-Wheel Drive Benefits:
Enhanced Traction: Four-wheel drive provides superior traction and control when navigating challenging terrains, such as deep mud or flooded areas.
Off-Road Capability: This system is particularly suitable for off-road enthusiasts and vehicles designed for rugged adventures.
All-Wheel Drive Benefits:
- General Driving Conditions: All-wheel drive is the preferred mode for regular driving, offering improved stability and traction on various road surfaces.
- Variable Torque Distribution: The system optimally distributes power to all four wheels, enhancing performance and safety in adverse weather conditions.
Considerations:
- On-Road Cornering: Four-wheel drive may make on-road cornering more challenging due to the synchronization of wheel speeds, which is not ideal for regular driving.
- Fuel Efficiency: All-wheel drive systems can be more fuel-efficient on regular highways by sending power primarily to the rear wheels.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between four-wheel drive and all-wheel drive is crucial for choosing the right system based on driving needs. Four-wheel drive excels in off-road situations, while all-wheel drive offers superior performance and traction in general driving conditions. Each system has its advantages and considerations, so it’s essential to select the appropriate system based on specific driving requirements and terrain.
Read More: